Installing Detectable Warning Plates
July 18, 2022
AMA, California, and ISO 23599 standards for attention-style tactile paving
Read the full original article on reliance-foundry.com >
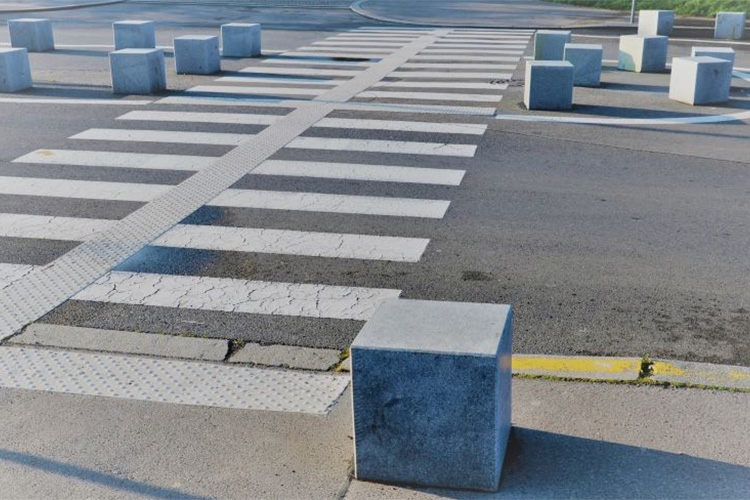

Here, “attention” pavers with domes guides walkers across the street: often “guidance” tile with long runners would be used instead.
Detectable warning plates are a type of tactile paving, designed to be “read” by those using a cane for guidance. They are a form of universal design, for their contrasting color and textures act as communication for all users of a space. Tiles with truncated domes were invented in Japan in the late sixties by Seiichi Miyake, and installed for the first time in 1967, outside a school for the blind. They have since been adopted worldwide, with basic installation standards to ensure that they communicate the same message to users the world over.
Tactile paving standards: the ADA, California’s Building Standards Code, and ISO 23599
Tactile paving tiles were originally called “tenji” blocks in Japan. Tenji is the word for a Japanese Braille system, and detectable warning plates—and other tenji, like directional guidance tiles—are, like Braille, a language system designed to communicate non-visually.
Languages need some standardization to be clear to users, and attention getting detectable warning plates are no different. There are several standards that offer slightly different design guidelines. The three in most common use in North America are the Americans with Disabilities Act standards, the California Building Standards Code, and ISO 23599—an international standard that is followed in jurisdictions from Ontario, Canada to Sweden.
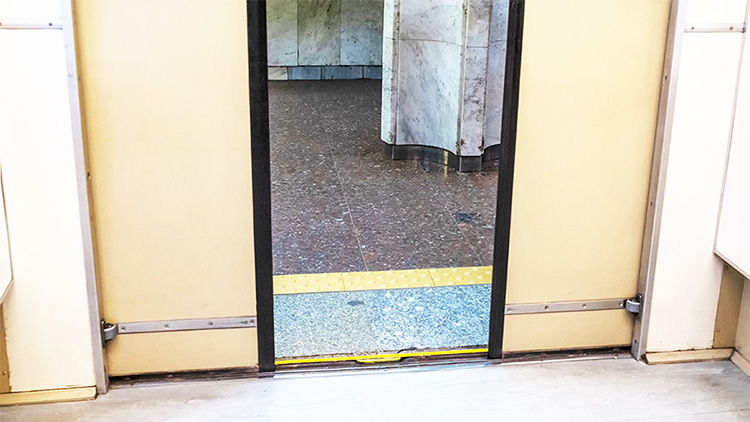

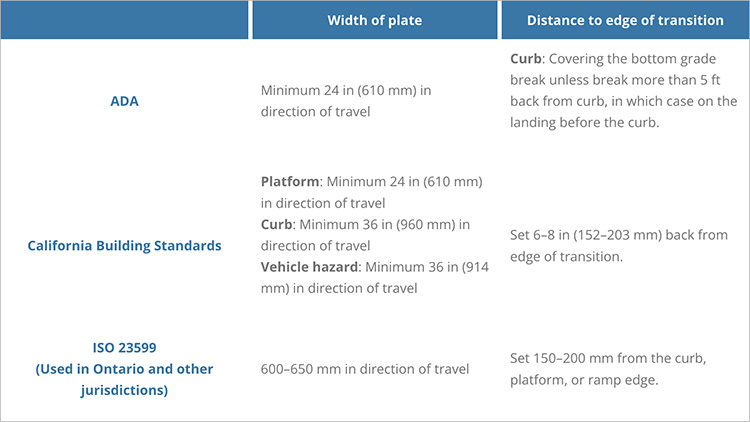
In some jurisdictions this strip of DWPs would need to be wider to comply with local building standards.
Detectable warning tile placement
All standards require detectable warning plates to be installed where there are dangerous changes in a walking surface. For example, they are a requirement at the edges of train, subway, and ferry platforms, where there might be a gap or hole that someone could fall into. Offset patterns are sometimes used in these locations. In offset tiles, the dots do not form a grid. Instead, each dome is centered on the gap between domes of the row above. Although offset patterns are often used before a gap, they are not a consistent marker. Sometimes a simple grid is used.
Attention-getting plates are also placed where there is a change in the grade of the surface, especially where there are vehicle hazards. For example, tactile pavers are placed at the top of steep ramps and on the landings. They are also used on curb cuts, at the end of the ramp, just before the street.
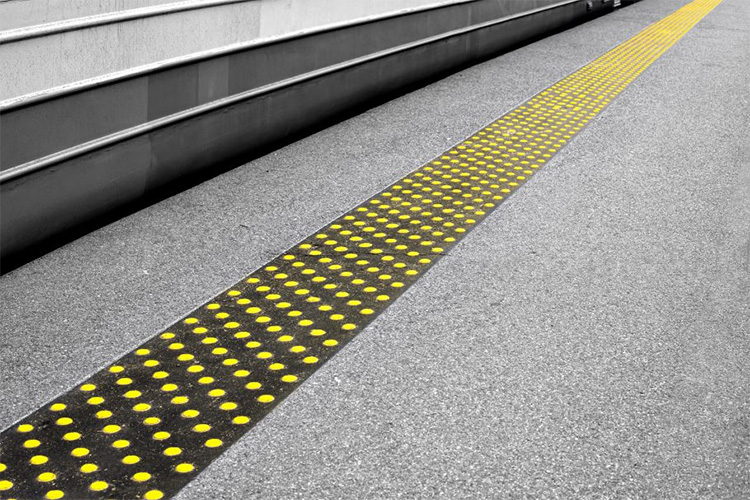

Truncated domes in an offset pattern in on a subway platform.
Dome size
Domes on detectable warning plates are known as “truncated domes” because they do not form a full round bubble. A little bit of flattening on the top makes them less slippery and dangerous to pedestrians.
Indoor truncated domes tend to be shorter than outdoor ones. Four millimeters is common for indoor spaces, and five for outdoors. However, different standards have slightly different appropriate ranges. The following table offers the specifications for domes in each of the three major North American standards.
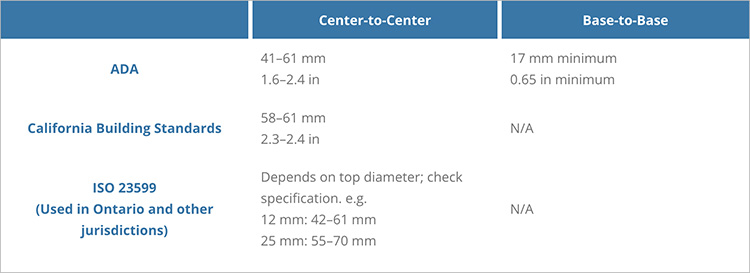
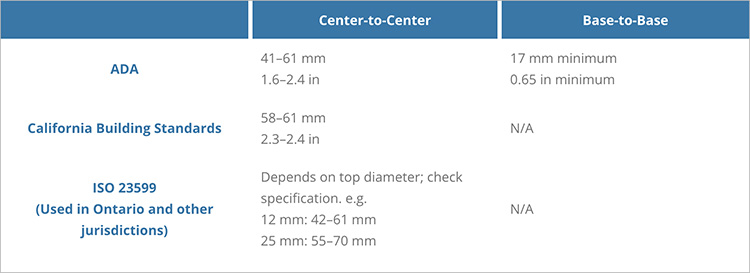
Dome spacing
Dome spacing is an important design consideration for a few reasons.
The space between domes is important to catch and guide canes. Large gaps could read as directional indicators or cause a person to miss an upcoming drop. Gaps that are too small could read as a bumpy surface, if the cane did not dip sufficiently between domes.
Additionally, these are paving plates, designed to be walked on in all sorts of weather conditions. Those built into curb cuts and on ramps cannot be slippery. Appropriate spacing between domes helps increase the friction of the surface. Most plates also have roughening bumps on plate and domes to help prevent slips and falls.
Methods of installing detectable warning plates
Detectable warning plates come in a variety of materials and finishes depending on where they’re being installed.
Unpainted raw cast DWPs are commonly used outside, where they are usually laid into new concrete. This cast-in-place installation method is the most durable, as the concrete helps cure the plate into the hardscape. Cast iron stands up well to heavy traffic, snowplows, and other hard wear.
In cast-in-place installations, lifting springs are used to lower the tactile pavers into the concrete. A rubber mallet can be used to help level the plate. An edger can create a small gap for thermal expansion, and the surrounding concrete troweled and brushed flat. The detectable warning plate becomes solidly affixed as the concrete hardens.
Most heavy cast-iron plates are installed with this method. Lighter, thinner surface tiles made of other material (like fiberglass, resins, or plastic) might be installed instead with adhesive and bolt-through fasteners.

A grid pattern in cast iron detectable warning plates warn of vehicle hazards on the street.
Universal design and public spaces
Reliance Foundry offers ADA compliant cast iron detectable warning plates in a range of sizes. Choose interlocking tiles or those featuring individual placement. Radial plates can be used to help cover a flare or curve in a curb. Square and rectangular plates can be used together to customize size. All our plates are designed to be cast-in-place during installation.
All specifications require DWPs to be of a contrasting color to the pavers or concrete around it. Most often, our cast iron is shipped raw: over time, it develops a red-brown patina that offers a sharp contrast to lighter concrete and pavers. For applications with darker concrete, asphalt, or red-brown bricks or stones, finishing with a contrasting paint like safety yellow brings the DWPs into compliance with the major standards.
Detectable warning plates offer guidance to those with vision impairment, but they are useful for all users. A change in the walking surface queues pedestrians to slow down and pay attention; contrasting color offers a visual topographical clue. This universal design, creating safety and ease in the built environment, welcomes all people into public spaces.
@reliancefoundry #reliancefoundry #bollards
Company:  Reliance Foundry Co. Ltd.
Reliance Foundry Co. Ltd.
Source: https://www.reliance-foundry.com/blog/installing-detectable-warning-plates
Tags:
Bollards
How can you customize a bike rack to incorporate your logo? (May 27, 2022), Bollard Installation Tricks: How to Install into Pavers (May 16, 2022), Spring is a perfect time to add colors and freshen up your outdoor space (April 11, 2022), Tactile paving makes the built environment more universally accessible (February 25, 2022), Shallow Mount Bollards - When and why choose shallow mount versus deep mount (December 15, 2021), Architectural lighting bollards: a blending of form and function (October 1, 2021), Hardscape: Urban Design and the Outdoor Bench (September 3, 2021), Thoughtful hardscape design can turn the concrete jungle into comfortable human habitat (July 21, 2021), Designer…Traffic Guides? Unique Spaces, Custom Bollards (June 25, 2021), Flexible Bollards vs. Traffic Delineators: which traffic safety equipment will provide best value for your application? (May 17, 2021)
Landscape Design
Safety
Traffic
How can you customize a bike rack to incorporate your logo? (May 27, 2022), Temporary Overlay Markers (TOM) - Road Markers (May 25, 2022)

